Enterprise Architecture Perspectives
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is about the organizational and technological entities in an enterprise, and the relations between them. As an activity, the goal of EA is to improve how all these entities support the business and IT goals in a better way, not just solution by solution, project by project, but for the business as a whole.
Each of these perspectives are assessed, evaluated and defined in several phases, both with respect to today’s situation and the target architecture.
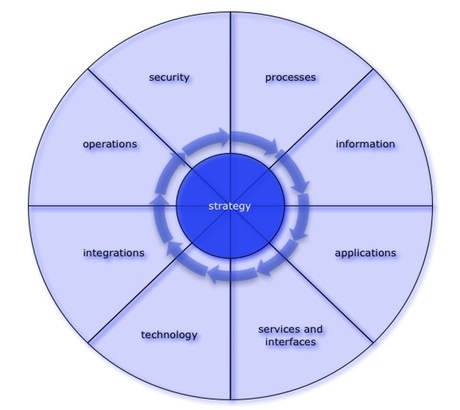
processes (business architecture)
- process maps
- identification of business process improvement candidates
- target business process designs
information (information architecture)
- capturing the concepts flowing through the essential business processes
- defining an information model supporting future processes
- enabling masterdata management
- enalbing the definition of a common domain model in a service oriented architecture
applications (functional application architecture)
- which applications are used by which users, in which business units, supporting which functions
- evaluating consolidation vs. best-of-breed options
- information architecture and application architecture – assessing scattered information entities and defining which applications should master which data
services and interfaces
- service composition architecture
- high level interfaces between business critical applications
- information architecture and SOA – using business language to build a common information model across all system specific information models
technology (infrastructure/technology architecture)
- the systems supporting the applications
- the platforms supporting application deployment
- the platforms supporting service and integration implementation
- the platforms supporting business process management
integrations
- integration scenarios and integration architecture patterns
- when to think SOA, EAI, ETL or simply point-to-point
- integration technologies, protocols etc.
- wholistic integration strategy
operations
- infrastructure locations and outsourcing
- operational risks and vulnarability
- adapting infrastructure and operations to risks
security
- securing processes, data, services and applications
- balancing freedom of roles with needs of access
- combining single-sign-on with service orientation
- network zoning
